Aci Fabric Command

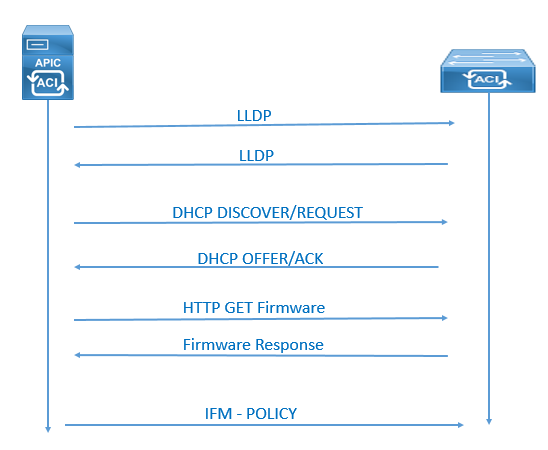
Aci uses inter fabric messaging ifm to communicate between the different nodes ifm uses tcp packets which are secured by 1024 bit ssl encryption and the keys are stored on secure storage.
Aci fabric command. It does this at the ingress interface of the first leaf switch connected to the endpoint. The cisco manufacturing certificate authority cmca signs the keys. Ls aci system controllers show fabric membership executing command. This command configures a vpc domain consecutively for a selected set of leaf node pairs.
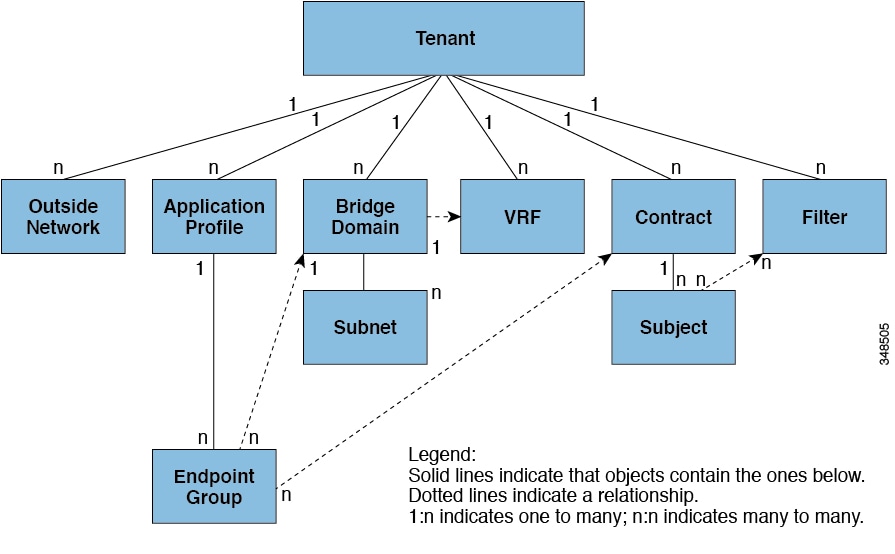
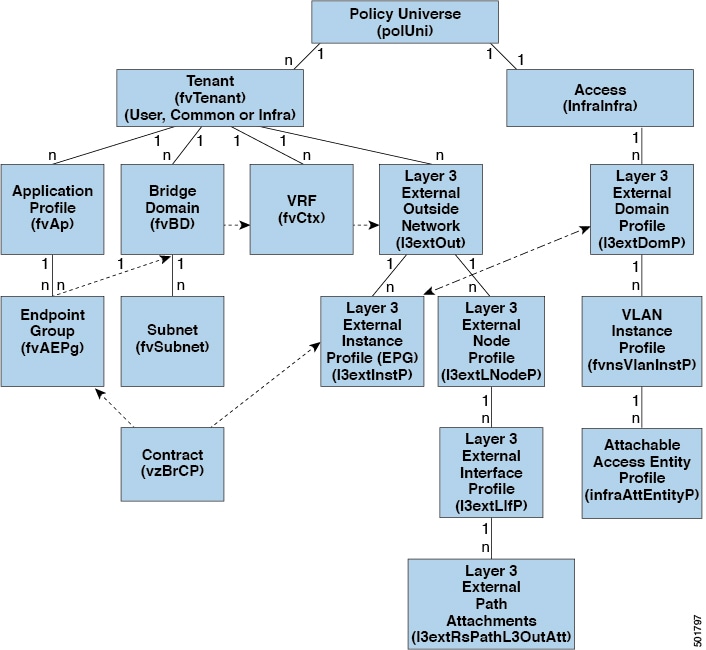
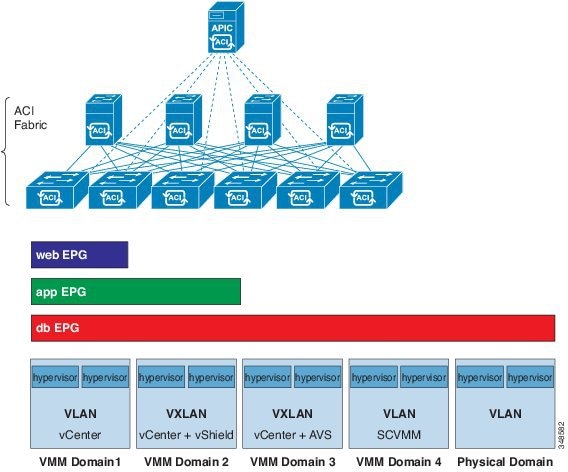
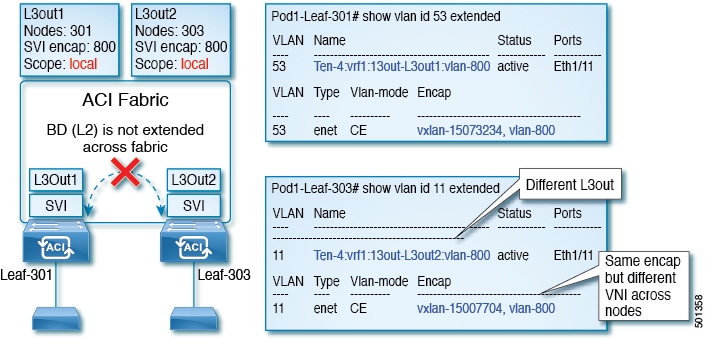
The consecutive and reciprocal options allow auto configuration of a vpc domain across all leaf nodes in the aci fabric. Another one is the layer 3 out l3out or external routed network in cisco apic gui prior to the apic release 4 2 which is to provide layer 3 l3 connectivity between servers connected to aci and other network domains outside of the aci fabric through routing. Some of these components include bridge domains bds and endpoint groups epgs to provide layer l2 connectivity or default gateway functions for a group of endpoints. All of the ingress interfaces across the fabric share the same router ip address and mac address for a given.
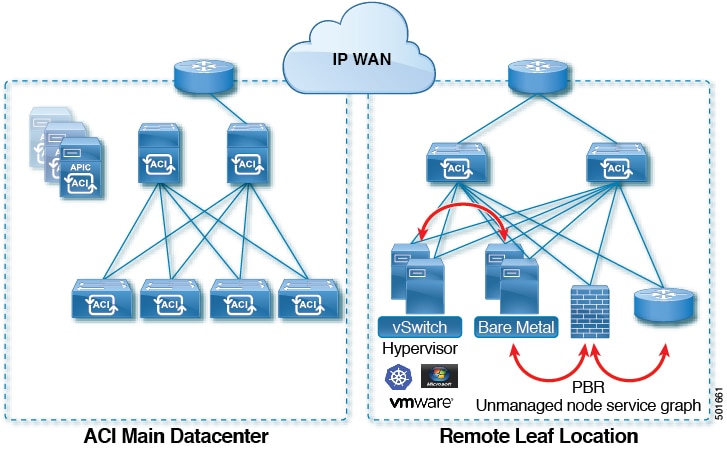
Issues with ifm can prevent fabric nodes communicating and from joining the fabric. Multiple sites buildings or rooms can span distances that are not serviceable by enough fiber connections or are too costly to connect each leaf switch to each spine switch across the sites. Vpc domain consecutive domain start leaf start node end node. In multi site scenarios full mesh connectivity may be not possible or may be too costly.
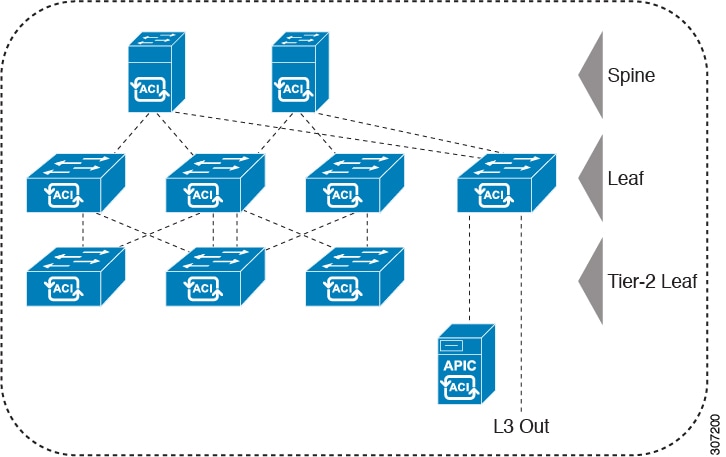
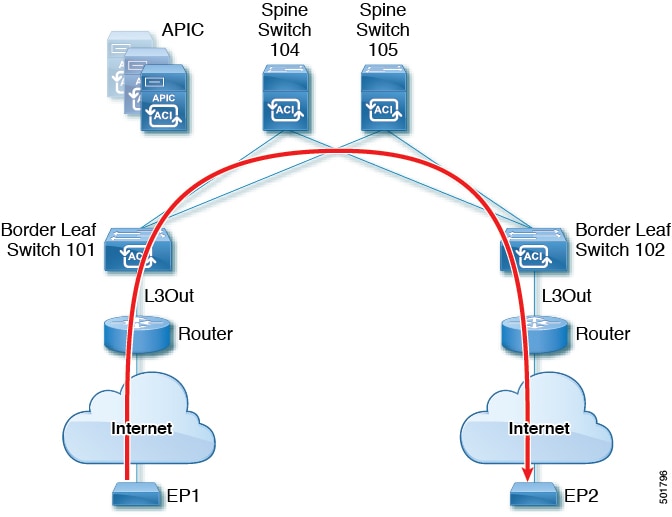
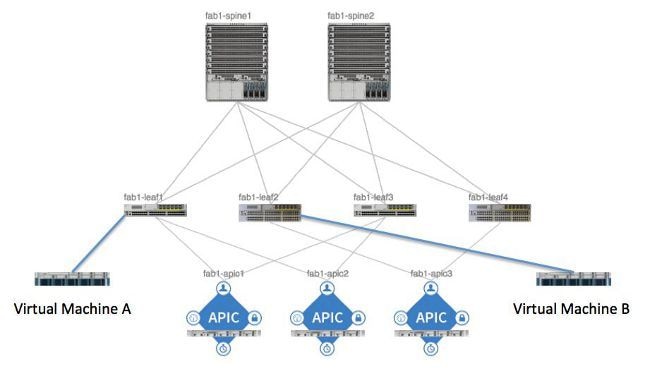
Typically an aci fabric implementation is a single site where the full mesh design connects each leaf switch to each spine switch in the fabric which yields the best throughput and convergence. The aci fabric is formed from multiple components. For each tenant the fabric provides a virtual default gateway that spans all of the leaf switches assigned to the tenant.